Energy-Efficient Glass Windows are revolutionizing building design and significantly impacting energy consumption. These windows, available in various forms like double-pane, triple-pane, and low-E options, leverage innovative technologies to reduce energy loss. Understanding their diverse types, performance characteristics, and installation details is key to optimizing energy efficiency in homes and businesses.
From the fundamental principles of how they work to the practical considerations of installation and maintenance, this guide will explore the world of energy-efficient windows. We’ll examine their performance, construction, benefits, and future trends to equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about window choices.
Introduction to Energy-Efficient Glass Windows
Source: americandeluxewindows.com
Energy-efficient glass windows are crucial for modern buildings, minimizing energy consumption. However, a building’s overall resilience also hinges on the materials used, like fire-resistant roofing materials, which play a vital role in protecting structures from damage. Choosing Fire-Resistant Roofing Materials alongside energy-efficient windows ensures a well-rounded approach to building safety and sustainability. Ultimately, the interplay of these features contributes to a more environmentally responsible and structurally sound building.
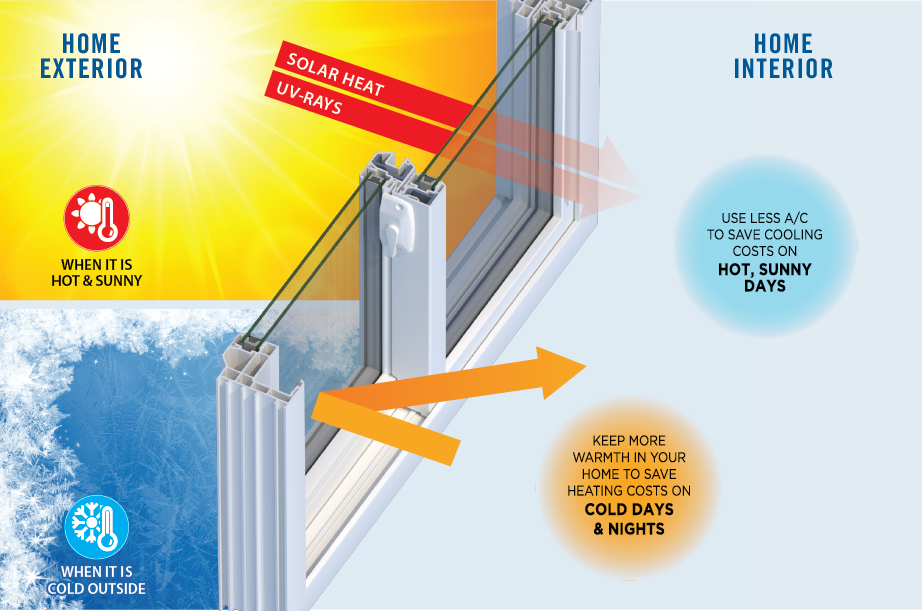
Energy-efficient glass windows are designed to minimize heat transfer between the indoor and outdoor environments, thereby reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. This translates to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint. Proper selection and installation of these windows are crucial for achieving these energy savings.
Energy-efficient windows use various techniques to trap heat within a building during winter and prevent excessive heat gain in summer. This helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature with minimal reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems. Different types of glass and construction methods are employed to achieve these goals, each with varying degrees of performance and cost.
Types of Energy-Efficient Glass Windows
Different types of energy-efficient glass windows employ various techniques to optimize energy performance. Common types include double-pane, triple-pane, and low-e coated glass. Each design has unique characteristics impacting its energy-saving capabilities and cost.
Double-Pane Windows
Double-pane windows consist of two panes of glass separated by an air space. This air gap acts as insulation, reducing heat transfer compared to single-pane windows. The air space also helps minimize condensation and noise. Double-pane windows are a common and relatively affordable option for energy efficiency.
Triple-Pane Windows
Triple-pane windows utilize an additional pane of glass and air space compared to double-pane windows. This increased insulation significantly reduces heat transfer, leading to higher energy savings, especially in extreme climates. However, triple-pane windows generally come with a higher price tag than double-pane windows.
Low-Emissivity (Low-E) Coated Glass
Low-Emissivity (Low-E) coated glass windows have a thin metallic coating applied to one or both glass surfaces. This coating reflects infrared radiation, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency. Low-E windows are often used in conjunction with double or triple-pane construction for enhanced performance. This technology is particularly effective in preventing heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer.
Comparative Analysis of Energy-Efficient Windows
| Window Type | Energy Savings (%) | Cost | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Double-pane | 20-30% | Moderate | Low |
| Triple-pane | 30-45% | High | Low |
| Low-E Double-pane | 25-40% | Slightly higher than double-pane | Low |
| Low-E Triple-pane | 40-55% | Highest | Low |
The table above provides a general comparison. Actual energy savings can vary based on climate, window size, and building design. Cost considerations also depend on the specific materials and features of each window type. Maintenance requirements for all types are generally low.
Performance Characteristics
Energy-efficient windows are designed to minimize heat transfer, improving thermal comfort and reducing energy consumption. Their performance is primarily evaluated through specific metrics, allowing for comparison and selection based on desired outcomes. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for informed decisions about window installation and design.
Window performance is influenced by a variety of factors. These include the materials used, the construction techniques employed, and the specific design features implemented. Different climates will also impact the effectiveness of various window types, demanding consideration of local conditions for optimal energy savings.
Thermal Performance
Energy-efficient windows excel in minimizing heat transfer, primarily through their U-value and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC). The U-value quantifies the rate of heat transfer through a material, and a lower U-value signifies better insulation. SHGC measures the amount of solar radiation that passes through the window, influencing both heat gain and heat loss.
Lower U-values and lower SHGC values indicate better energy efficiency.
Impact of Window Orientation
Window orientation significantly affects energy efficiency. South-facing windows in temperate climates can harness solar energy for heating in winter, but excessive heat gain in summer can necessitate additional cooling measures. North-facing windows generally provide less solar heat gain throughout the year, leading to reduced heating and cooling demands. East and west-facing windows experience varying amounts of solar gain depending on the time of day, influencing the heating and cooling needs.
Impact of Window Size
Larger windows, while providing more natural light, increase the surface area through which heat can be transferred. Therefore, a careful consideration of window size is essential, balancing the desire for natural light and open views with the need for energy efficiency. The balance between light and energy needs to be optimized to achieve the most favorable outcome.
Comparison of Glass Types in Different Climates
Different types of energy-efficient glass perform differently in varying climates. Low-Emissivity (Low-E) coatings, for instance, reduce heat transfer by reflecting infrared radiation. Double-pane windows, with an air gap between two panes, are effective in reducing heat transfer. The effectiveness of these types depends on the specific construction and the climate’s characteristics.
Performance Metrics Table
| Window Type | Climate | U-Value (W/m²K) | SHGC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-E, double-pane | Cold (e.g., Northern US) | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| Low-E, double-pane | Hot (e.g., Southern US) | 1.0 | 0.3 |
| Double-pane | Cold (e.g., Northern US) | 2.5 | 0.7 |
| Double-pane | Hot (e.g., Southern US) | 2.5 | 0.6 |
*Note: Values are illustrative examples and may vary based on specific window construction and manufacturer. Climate data is generalized for this example.
Construction and Materials
Energy-efficient windows are meticulously crafted to minimize heat transfer and maximize comfort while reducing energy consumption. Their construction involves a layered approach, carefully selecting materials and employing sophisticated sealing techniques. Understanding these aspects is key to appreciating the performance of these windows.
The design of energy-efficient windows prioritizes a multi-layered approach to thermal insulation. This approach, carefully balancing materials and construction techniques, significantly reduces energy loss. Different configurations are employed to achieve optimal performance in diverse climates.
Glazing
The glazing system is a critical component of energy-efficient windows. It directly impacts the window’s thermal performance. Multiple panes of glass, often with a low-emissivity (low-e) coating, are strategically positioned to minimize heat transfer. This configuration traps warm air within the window, enhancing insulation. Furthermore, the type of glass plays a significant role. Double or triple-pane windows are common choices, offering improved insulation. Specialized glass coatings can further reduce heat transfer and improve solar control.
Frames
Frame materials significantly impact a window’s thermal performance and longevity. High-performance windows often utilize thermally broken frames. This technique isolates the different parts of the frame to prevent heat transfer, enhancing overall insulation. Common frame materials include aluminum, vinyl, and wood. Aluminum frames are typically more affordable, while vinyl offers excellent durability and low-maintenance properties. Wood frames, while often more expensive, provide a traditional aesthetic and can have high thermal resistance.
Seals
Airtight seals are paramount in maintaining the energy efficiency of windows. These seals form a barrier against air infiltration, preventing drafts and heat loss. Specialized sealants and gaskets are used to create a complete seal around the window perimeter. Proper installation of these seals is crucial to the window’s effectiveness. Regular inspection and maintenance of seals are vital to ensure their continued functionality.
Materials and Durability
A variety of materials contribute to the construction of energy-efficient windows. Glass types, frame materials, and sealants are carefully selected to optimize performance and durability. Factors such as climate, environmental conditions, and intended use significantly influence the selection process. For instance, regions with harsh winters require windows with enhanced thermal resistance, while regions with high humidity might need specialized sealants resistant to moisture.
Selection for Different Climates
The choice of materials for energy-efficient windows is highly dependent on the specific climate and environmental conditions. In regions with extreme temperatures, such as those experiencing very cold winters, windows with multiple panes of low-e glass and thermally broken frames are often necessary. Conversely, in regions with high humidity, windows with specialized moisture-resistant sealants are preferable. This ensures long-term performance and durability. A careful assessment of local conditions is essential for optimal selection.
Benefits and Applications
Energy-efficient windows offer a compelling blend of environmental and economic advantages, making them a smart choice for various building types. Their ability to reduce energy consumption translates directly to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint. Beyond these core benefits, the diverse applications of these windows extend from residential homes to large commercial structures.
Environmental Benefits, Energy-Efficient Glass Windows
Energy-efficient windows significantly reduce a building’s reliance on external heating and cooling systems. By minimizing heat transfer through the glass, they contribute to a lower carbon footprint, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This translates to a smaller environmental impact compared to buildings using conventional windows. The reduced energy consumption also decreases the demand for fossil fuels, which further benefits the environment.
Economic Benefits
The reduced energy consumption associated with energy-efficient windows translates directly into substantial economic savings. Lower energy bills are a primary benefit, and these savings can be substantial over the lifespan of the window. For instance, a home equipped with energy-efficient windows could see a notable reduction in their annual heating and cooling costs. The long-term financial advantages make energy-efficient windows a worthwhile investment for both residential and commercial structures.
Applications of Energy-Efficient Windows
Energy-efficient windows are applicable across a broad spectrum of building types. Their benefits extend from the comfort and efficiency gains in residential homes to the operational savings and sustainability measures in commercial spaces.
Residential Applications
Energy-efficient windows enhance comfort and reduce energy costs in homes. Improved insulation reduces the need for heating and cooling, leading to lower utility bills. The enhanced thermal performance also contributes to a more comfortable indoor environment, irrespective of the external weather conditions. A well-insulated home with energy-efficient windows will likely experience lower energy consumption throughout the year.
Commercial Applications
Energy-efficient windows play a crucial role in reducing energy consumption in commercial buildings. In office spaces, optimized thermal performance can lead to substantial savings on cooling and heating expenses. Retail spaces and other commercial structures can also realize significant reductions in their energy consumption, thus improving their bottom line and sustainability profile. The implementation of energy-efficient windows in commercial buildings can demonstrably reduce operational costs.
Examples of Successful Implementations
Numerous buildings have successfully implemented energy-efficient windows. For example, several modern office buildings have seen notable reductions in their energy bills after installing these windows. Similarly, numerous residential projects have demonstrated a considerable decrease in energy consumption due to the adoption of energy-efficient windows. This showcases the practical and widespread application of this technology.
Benefits and Applications Table
| Benefit | Application | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced energy bills | Residential | Lower heating and cooling costs, potentially saving hundreds of dollars annually. |
| Environmental friendliness | Commercial | Reduced carbon footprint, contributing to a more sustainable operation. |
| Enhanced thermal comfort | Residential | Improved indoor temperature regulation, reducing the need for frequent adjustments. |
| Improved insulation | Commercial | Reduced energy consumption, leading to lower operational costs. |
| Increased natural light | Residential and Commercial | Improved daylight penetration, reducing the need for artificial lighting and promoting well-being. |
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for maximizing the energy-saving potential of energy-efficient windows. These steps ensure the windows perform as intended and maintain their insulation properties over time, contributing to long-term energy savings. A well-installed and maintained window system can significantly reduce energy consumption and enhance comfort.
Installation Steps
Careful installation is paramount for optimal window performance. Incorrect installation can lead to thermal bridging, reducing the window’s insulating properties and negating energy savings. Adhering to manufacturer’s instructions is vital.
- Site Preparation: Thorough preparation of the window frame and surrounding area is essential. This involves ensuring the wall is properly prepared for the window frame installation and that the window sill is level and plumb. Properly preparing the site prevents future problems and ensures a solid foundation for the window.
- Framing and Sealing: The window frame must be securely fitted into the opening, with all gaps properly sealed. High-quality sealant ensures a tight fit, preventing drafts and improving energy efficiency.
- Glazing and Weatherstripping: The glass panes must be securely fastened in the frame. High-quality weatherstripping around the window frame further enhances the seal, preventing air leakage and improving insulation.
- Inspection and Adjustment: A final inspection confirms proper installation and alignment. Any necessary adjustments are made before finalizing the installation.
Maintenance Guidelines
Regular maintenance helps preserve the energy efficiency of windows over time.
- Cleaning: Regular cleaning of the window panes removes dirt and grime, which can reduce the effectiveness of the glazing. Cleaning should be done regularly, using appropriate cleaning solutions to avoid damaging the window material.
- Checking for Leaks: Periodically inspect the window for any signs of air leaks or drafts. Address any issues promptly to maintain the window’s energy efficiency.
- Weatherstripping Maintenance: Inspect and replace weatherstripping if needed. Damaged or worn weatherstripping reduces the seal around the window, potentially leading to increased energy loss. Regular checks and replacement are key to maintain the energy efficiency of the window.
- Frame Inspection: Regular inspection of the window frame and surrounding areas for any signs of damage or deterioration is important. Addressing these issues promptly prevents further damage and maintains the window’s structural integrity, which contributes to its long-term energy efficiency.
Importance of Proper Installation
Proper installation ensures the window meets the design specifications for energy efficiency. This includes a tight seal to minimize air infiltration, proper alignment to prevent thermal bridging, and correct fastening to avoid structural issues.
“Proper installation is the cornerstone of energy-efficient window performance. It maximizes the window’s ability to block drafts and regulate temperature, resulting in significant energy savings.”
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for maintaining the energy-efficient properties of the window. It involves consistent cleaning, inspection for leaks, and addressing any issues promptly. Ignoring maintenance can lead to significant energy loss over time.
“Regular maintenance of energy-efficient windows is vital for preserving their energy-saving potential. This translates into sustained cost savings on energy bills and minimizes the need for costly repairs.”
Future Trends and Developments
The realm of energy-efficient glass windows is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in materials science and the need for sustainable building practices. Emerging technologies are poised to further enhance the performance and functionality of these crucial building components. This section explores these promising trends, highlighting the potential impact of smart window technologies and advanced materials on future window designs.
The future of energy-efficient windows lies in integrating innovative technologies to optimize energy savings and enhance occupant comfort. This involves not only improving existing materials but also incorporating smart features and advanced coatings that dynamically respond to changing environmental conditions.
Emerging Technologies in Energy-Efficient Window Design
The development of energy-efficient windows is intrinsically linked to the exploration of new materials and functionalities. This includes innovations in glass composition, coatings, and the integration of smart technologies. A key aspect of these innovations is the potential for increased energy savings, reduced reliance on conventional heating and cooling systems, and enhanced occupant comfort.
Potential Future Advancements in Glass Technology for Energy Efficiency
Significant advancements are expected in glass technology. These include the development of more complex layered glass structures with specialized coatings to further enhance thermal insulation and light control. These structures may also include self-cleaning properties to maintain window clarity and minimize the need for frequent cleaning.
Impact of Smart Window Technologies on Energy Efficiency
Smart windows are rapidly gaining traction. These windows can dynamically adjust their properties, such as light transmission and reflectivity, in response to environmental conditions. This dynamic control optimizes energy use by reducing heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter. Smart windows can also be integrated into building management systems, enabling precise control over indoor climate and further enhancing energy efficiency. For instance, a smart window might automatically darken during the day to reduce heat gain, then lighten at night to allow for natural light.
Role of Advanced Materials in Improving Energy-Efficient Windows
Advanced materials play a pivotal role in the development of more efficient windows. These materials are crucial for enhancing thermal insulation, light control, and overall window performance. Examples include the use of low-emissivity (low-e) coatings and innovative glass laminates. Furthermore, the use of sustainable materials in the window frame construction will further enhance the overall sustainability profile.
Table of Emerging Technologies in Energy-Efficient Windows
| Technology | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Smart windows | These windows incorporate electrochromic or thermochromic materials that adjust their light transmission and reflectivity in response to external conditions. They can be programmed to darken or lighten, thereby controlling solar heat gain and reducing energy consumption. | Significant reduction in energy consumption for heating and cooling. Enhanced occupant comfort by dynamically adjusting light and heat. |
| Advanced coatings | Low-e coatings are increasingly sophisticated, with new formulations that enhance their ability to reflect heat and ultraviolet (UV) radiation while allowing visible light to pass through. This translates into improved thermal insulation and reduced heat transfer. Further development includes self-cleaning coatings to minimize maintenance requirements. | Improved thermal insulation, reduced heat transfer, reduced energy consumption, and potentially enhanced UV protection. |
| Advanced glass laminates | These involve layering different types of glass with specialized interlayers to enhance safety, security, and energy efficiency. The interlayers can include polymers that further reduce heat transfer and enhance soundproofing. | Increased safety and security. Improved thermal insulation. Potentially enhanced soundproofing. |
Closure: Energy-Efficient Glass Windows
In conclusion, energy-efficient glass windows offer a compelling blend of environmental responsibility and economic benefits. Their performance, encompassing thermal efficiency, durability, and various applications, makes them a worthwhile investment for both residential and commercial buildings. The future of window technology promises even greater advancements, driven by innovative materials and smart technologies, further enhancing their impact on sustainable practices.
FAQs
How do different window types compare in terms of cost?
Triple-pane windows, while offering the highest energy savings, generally come with a higher upfront cost than double-pane windows. Low-E windows typically fall between these two in terms of price.
What is the impact of window size on energy efficiency?
Larger windows can lead to increased energy loss, especially if not properly insulated. Careful consideration of window size and placement, along with the use of energy-efficient glass, is crucial for optimizing energy efficiency.
What are the key maintenance steps for energy-efficient windows?
Regular cleaning, checking for any cracks or damage, and ensuring seals are intact are vital for maintaining optimal energy performance. Consult your window manufacturer’s recommendations for specific maintenance guidelines.
What are some emerging technologies in energy-efficient window design?
Smart windows, incorporating electrochromic materials, can dynamically adjust their transparency to control solar heat gain. Advanced coatings further enhance reflectivity and reduce heat transfer, enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Energy-efficient glass windows are crucial for modern building design, aiming for reduced energy consumption. Considering the broader picture, materials like those used in sustainable roof systems, like the ones detailed at Sustainable Roof Materials , are equally important for overall building sustainability. Ultimately, both strategies contribute to a more eco-conscious approach to constructing energy-efficient buildings.
Energy-efficient glass windows are crucial for modern building design, and their performance is significantly impacted by the overall building envelope. This directly connects to modern roofing styles, as the interplay between the window and roof is key to maximizing energy efficiency. For instance, choosing the right roofing materials and designs in harmony with Modern Roofing Styles can significantly reduce heat gain or loss through the building’s exterior, ultimately enhancing the performance of energy-efficient glass windows.
Energy-efficient glass windows are crucial for modern buildings, but their performance can be significantly boosted by innovative design choices. For instance, integrating them with unique roof structures, like the ones featured on Unique Roof Structures , can optimize natural light and ventilation, further enhancing the energy efficiency of the entire building. Ultimately, these smart design approaches translate into significant savings for homeowners and businesses.
Energy-efficient glass windows are crucial for sustainable homes. They significantly reduce energy consumption, making them a vital component of eco-friendly construction. Consider the complementary benefits of Green Concrete for Eco-Friendly Homes which, when used in conjunction with these windows, can optimize overall home energy performance. Ultimately, these advancements in building materials are key to achieving truly sustainable architecture.
Energy-efficient glass windows are crucial for modern buildings, offering excellent insulation. To maximize this insulation, considering weatherproof wall materials like those detailed in Weatherproof Wall Materials is key. Properly selected and installed window systems, along with weatherproof walls, are the cornerstone of sustainable building design and contribute significantly to overall energy efficiency.
